Wireless Application Protocol (WAP) in Mobile Computing
Wireless Application Protocol or WAP is a programming model or an application environment and set of communication protocols based on the concept of the World Wide Web (WWW), and its hierarchical design is very much similar to TCP/IP protocol stack design. See the most prominent features of Wireless Application Protocol or WAP in Mobile Computing:
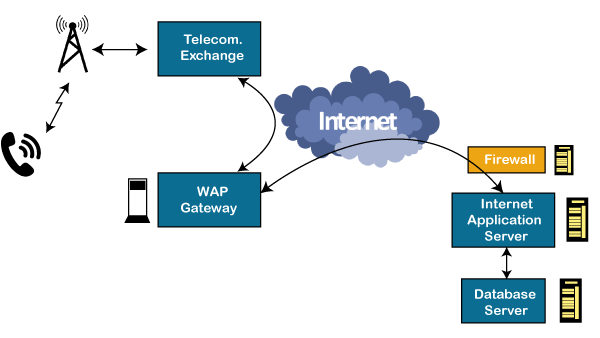
- WAP is a De-Facto standard or a protocol designed for micro-browsers, and it enables the mobile devices to interact, exchange and transmit information over the Internet.
- WAP is based upon the concept of the World Wide Web (WWW), and the backend functioning also remains similar to WWW, but it uses the markup language Wireless Markup Language (WML) to access the WAP services while WWW uses HTML as a markup language. WML is defined as XML 1.0 application.
- In 1998, some giant IT companies such as Ericson, Motorola, Nokia and Unwired Planet founded the WAP Forum to standardize the various wireless technologies via protocols.
- After developing the WAP model, it was accepted as a wireless protocol globally capable of working on multiple wireless technologies such as mobile, printers, pagers, etc.
- In 2002, by the joint efforts of the various members of the WAP Forum, it was merged with various other forums of the industry and formed an alliance known as Open Mobile Alliance (OMA).
- WAP was opted as a De-Facto standard because of its ability to create web applications for mobile devices.
Working of Wireless Application Protocol or WAP Model
The following steps define the working of Wireless Application Protocol or WAP Model:
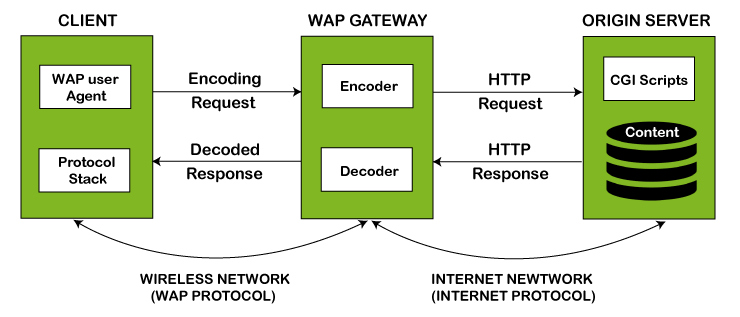
- The WAP model consists of 3 levels known as Client, Gateway and Origin Server.
- When a user opens the browser in his/her mobile device and selects a website that he/she wants to view, the mobile device sends the URL encoded request via a network to a WAP gateway using WAP protocol.
- The request he/she sends via mobile to WAP gateway is called as encoding request.
- The sent encoding request is translated through WAP gateway and then forwarded in the form of a conventional HTTP URL request over the Internet.
- When the request reaches a specified Web server, the server processes the request just as it would handle any other request and sends the response back to the mobile device through WAP gateway.
- Now, the WML file's final response can be seen in the browser of the mobile users.
WAP Protocol Stack
It specifies the different communications and data transmission layers used in the WAP model:
Application Layer: This layer consists of the Wireless Application Environment (WAE), mobile device specifications, and content development programming languages, i.e., WML.
Session Layer: The session layer consists of the Wireless Session Protocol (WSP). It is responsible for fast connection suspension and reconnection.
Transaction Layer: The transaction layer consists of Wireless Transaction Protocol (WTP) and runs on top of UDP (User Datagram Protocol). This layer is a part of TCP/IP and offers transaction support.
Security Layer: It contains Wireless Transaction Layer Security (WTLS) and responsible for data integrity, privacy and authentication during data transmission.
Transport Layer: This layer consists of Wireless Datagram Protocol (WDP). It provides a consistent data format to higher layers of the WAP protocol stack.
Advantages of Wireless Application Protocol (WAP)
Following is a list of some advantages of Wireless Application Protocol or WAP:
- WAP is a very fast-paced technology.
- It is an open-source technology and completely free of cost.
- It can be implemented on multiple platforms.
- It is independent of network standards.
- It provides higher controlling options.
- It is implemented near to Internet model.
- By using WAP, you can send/receive real-time data.
- Nowadays, most modern mobile phones and devices support WAP.
Disadvantages of Wireless Application Protocol (WAP)
Following is a list of some disadvantages of Wireless Application Protocol or WAP:
- The connection speed in WAP is slow, and there is limited availability also.
- In some areas, the ability to connect to the Internet is very sparse, and in some other areas, Internet access is entirely unavailable.
- It is less secured.
- WAP provides a small User interface (UI).
Applications of Wireless Application Protocol (WAP)
The following are some most used applications of Wireless Application Protocol or WAP:
- WAP facilitates you to access the Internet from your mobile devices.
- You can play games on mobile devices over wireless devices.
- It facilitates you to access E-mails over the mobile Internet.
- Mobile hand-sets can be used to access timesheets and fill expenses claims.
- Online mobile banking is very popular nowadays.
- It can also be used in multiple Internet-based services such as geographical location, Weather forecasting, Flight information, Movie & cinema information, Traffic updates etc. All are possible due to WAP technology.



